Understanding the Basics of Laser Welding Machine Technology
What is a Laser Welding Machine?
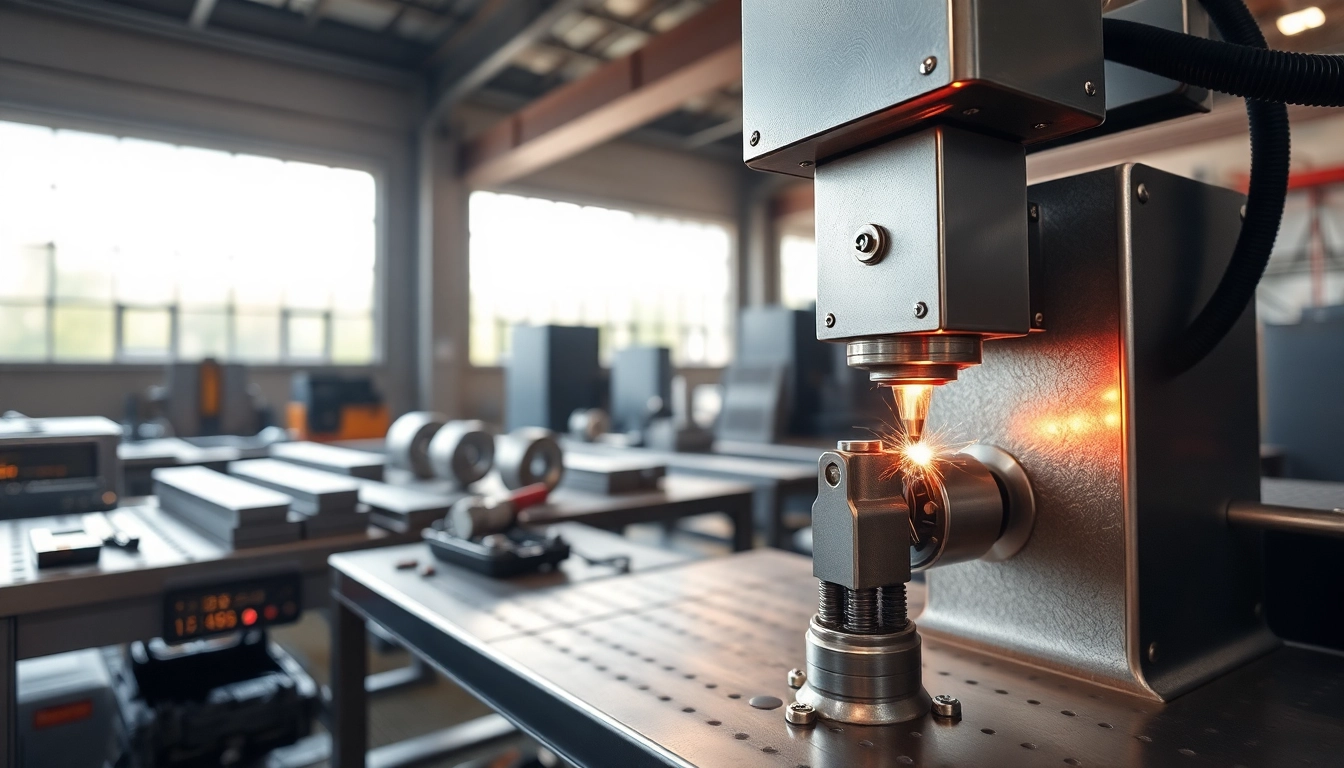
A Laser welding machine is a specialized piece of equipment used for efficiently and precisely joining materials through the application of laser technology. Unlike traditional welding methods that use an electric arc or gas flame to melt and fuse materials together, laser welding employs a high-powered laser beam to concentrate heat on a small area, creating a molten pool that leads to welding upon solidification. This technique can be applied to various materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics, making it a versatile solution in modern manufacturing.
How Does Laser Welding Work?
The fundamental principle of laser welding lies in its ability to focus a laser beam onto the materials being joined. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Laser Generation: The laser beam is generated by a laser source, such as a fiber or CO2 laser, which is then directed through optical components.
- Focusing: The laser beam is focused onto a small focal point, achieving extremely high energy density. This concentrated energy heats the material to its melting point rapidly.
- Joining Process: As the laser beam moves along the joint seam, it causes the base material to melt, forming a weld pool. The cooling of this molten pool solidifies the materials, creating a strong bond.
- Post-Weld Treatment: Depending on the application, post-weld heat treatment may be employed to relieve stress and enhance material properties.
Laser welding can be performed in various modes, such as conduction mode, keyhole mode, and hybrid mode, each suitable for different materials and thicknesses.
Common Applications of Laser Welding Machines
Laser welding machines find their application across a multitude of industries, owing to their precision and adaptability. Some notable sectors include:
- Aerospace: Laser technology is crucial for manufacturing aircraft components, ensuring strength and lightweight characteristics.
- Automotive: It is employed for welding parts like fuel tanks and catalytic converters, where precision is paramount.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Laser welding allows for sterile, precise joints in devices like surgical instruments and implants.
- Electronics: The welding of electronic components often requires the delicate handling capabilities that laser systems provide.
- Jewelry Production: Laser welding offers jewelers the ability to work on intricate designs with minimal heat distortion.
Advantages of Using Laser Welding Machine Over Traditional Methods
Increased Precision and Quality
One of the most compelling advantages of using a laser welding machine is the precision it offers. The focused nature of the laser beam allows for tight tolerances, resulting in clean, high-quality welds that require minimal post-processing. This precision reduces the likelihood of defects, such as porosity or distortion, which are more common in traditional welding methods. The ability to weld thin materials without burning them through is particularly useful in industries such as electronics and automotive.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Laser welding machines deliver higher efficiency compared to traditional welding methods. The speed of the welding process reduces cycle times significantly, allowing manufacturers to increase output without compromising quality. Additionally, the precision of laser welding minimizes material wastage, which can lead to lower overall material costs. Although the initial investment for a laser welding machine may be higher, the long-term savings in labor and production costs often justify the outlay.
Environmentally Friendly Processes
Laser welding is also an environmentally friendly option. Due to its higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption, the carbon footprint associated with the welding process is lower than that of traditional welding. Furthermore, the lack of filler materials in many laser welding applications reduces waste. Many laser welding systems are capable of operating with reduced emissions, making them a more sustainable choice for manufacturers seeking to meet environmental regulations.
Choosing the Right Laser Welding Machine for Your Needs
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a laser welding machine, several critical features should be considered to ensure it meets your specific application requirements:
- Laser Type: Different types of lasers (e.g., fiber, CO2) possess varying attributes. Fiber lasers are typically preferred for metal welding due to their high efficiency and improved quality.
- Power Rating: The power output of the laser determines its suitability for various materials and thicknesses. Higher power ratings allow for faster welding speeds and thicker materials.
- Control Systems: Advanced control systems can enhance the precision and repeatability of the welding process, providing options for integration with automation.
- Size and Weight: Depending on your workspace, the size and weight of the machine can be a key consideration, influencing mobility and installation requirements.
- Cooling Systems: Adequate cooling is essential to maintain performance and prevent overheating, so consider the built-in cooling mechanisms of the machine.
Budgeting for Your Laser Welding Machine
Budgeting for a laser welding machine involves considering not only the initial purchase price but also the long-term operational costs. Essential factors include:
- Purchase Price: Prices can vary significantly based on features, laser type, and manufacturer. Ensure you get a machine that offers the best value for capabilities.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance is critical for the longevity of the equipment, so factor in potential upkeep expenses.
- Operational Costs: Consider energy consumption and the potential need for additional training for operators, which can impact total expenses.
- Return on Investment: A well-planned implementation can lead to significant cost savings through efficiency gains, reduced waste, and improved product quality.
Top Industries Utilizing Laser Welding Machines
The versatility of laser welding technology enables its application across various industries, with some of the top sectors being:
- Aerospace and Defense: The need for precision and reliability in this industry makes laser welding an ideal choice for critical components.
- The growing trend towards electric vehicles has driven the demand for robust, lightweight materials that laser welding can accommodate.
- Electronics: Miniaturization of electronic components requires advanced techniques like laser welding to assemble devices with small tolerances.
- Medical: In the medical field, the increasing complexity of devices often necessitates the benefits of laser welding.
- Manufacturing: General manufacturing employs laser welding for various components, enhancing speed and efficiency.
Best Practices for Operating a Laser Welding Machine
Safety Measures and Protocols
Ensuring safety when operating a laser welding machine is paramount due to the associated risks, including eye damage and electric shock. Implementing stringent safety protocols can safeguard operators and bystanders:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators should wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses with laser filters, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Signage and Barriers: Clearly mark hazardous areas with appropriate signage and barriers to prevent unauthorized access during operation.
- Training: Regular training programs should be established to educate operators about safety procedures and emergency protocols.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce SOPs to guide operators in safe machine operation and maintenance practices.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance of the laser welding machine is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Key maintenance tips include:
- Regular Cleaning: Keeping the optical components clean is essential for optimal laser performance. Dust and residues can impede the laser beam quality.
- Calibration: Maintenance should include periodic calibration of the laser beam to ensure consistency in welding quality.
- Component Inspection: Regularly inspect key components like lenses, mirrors, and reflectors for wear or damage, replacing them as needed.
- Software Updates: Keeping the machine’s software up to date can enhance functionality and address potential security risks.
Training Operators to Use Laser Welding Machines
Comprehensive training programs are essential for operators to effectively and safely handle laser welding machines. Key aspects of training should include:
- Understanding Technology: Operators should be familiar with the principles of laser welding, including the operation of the laser and the effects of various parameters on the weld.
- Hands-On Practice: Providing practical training sessions helps operators gain confidence and competence in engaging with the machinery.
- Troubleshooting Skills: Training should include troubleshooting common issues, enabling operators to address problems that may arise during operation.
- Sustainability Practices: Educating operators on environmentally friendly practices can enhance the sustainability of the welding process.
The Future of Laser Welding Machine Technology
Innovations on the Horizon
The realm of laser welding technology is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in materials science, optics, and automation. Emerging innovations include:
- Increased Laser Efficiency: Research is ongoing to develop lasers with higher efficiency and power capabilities, allowing for even greater applications.
- Adaptive Laser Welding: Smart systems that adjust welding parameters in real-time based on feedback can enhance precision and reduce waste.
- Integration with Robotics: The integration of laser welding with robotic systems streamlines processes, enhancing production speed and flexibility.
- Digital Twin Technology: Utilizing digital twin models will enable manufacturers to simulate welding processes, optimizing settings before actual execution.
Impact on Various Industries
The advancements in laser welding technology are poised to revolutionize several sectors:
- Aerospace: The need for lighter and stronger materials as aerospace continues to innovate will see an increased adoption of laser technologies.
- Automotive: The shift towards electric vehicles will catalyze new design and manufacturing processes where laser welding plays a crucial role.
- Medical Devices: As complexity in medical devices increases, so does the demand for the precision welding capabilities offered by laser technology.
- Consumer Electronics: The trend toward smaller, more efficient devices is likely to increase reliance on laser welding in that industry.
Trends Shaping the Future of Welding
Several trends are emerging that shape the future of welding, particularly in relation to laser technology:
- Automation and Industry 4.0: The integration of IoT and smart manufacturing principles into welding processes will result in more connected, data-driven operations.
- Focus on Sustainability: As industries strive for environmental sustainability, laser welding technologies are expected to play a pivotal role in reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Customization: The ability to tailor welding parameters to specific applications will further expand the usage of laser welding technology in varied fields.
- Collaboration with AI: The potential use of artificial intelligence to enhance welding processes and predictive maintenance will revolutionize the operational capabilities of laser welding machines.