Understanding Veterinary X-Ray Systems
What is a Veterinary X-Ray System?
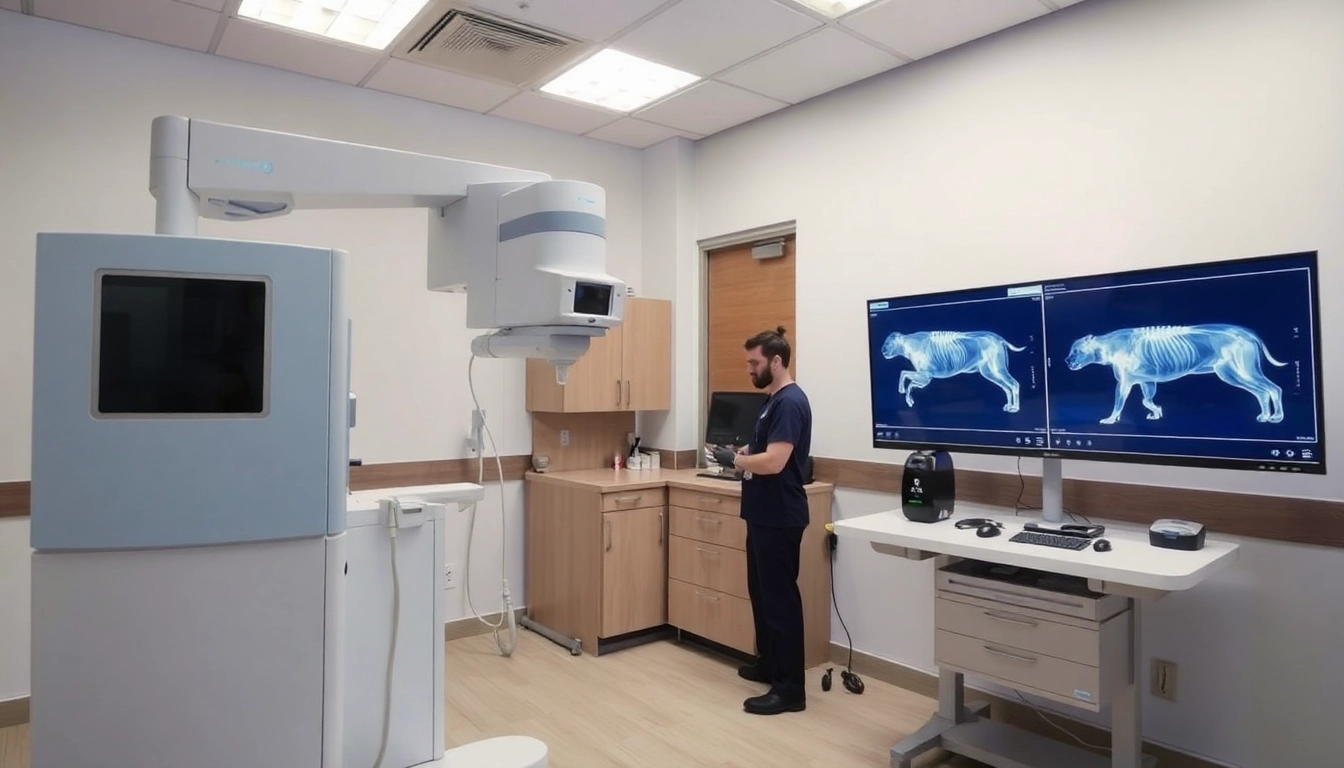
A veterinary x-ray system is an essential diagnostic tool that employs radiographic technology to produce images of an animal’s internal structures. This system allows veterinarians to visualize bones, tissues, and organs swiftly, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various ailments. Through electromagnetic radiation, x-rays penetrate the body and create images on a film or digital receptor, highlighting potential issues like fractures, tumors, or foreign bodies. Unlike human x-ray systems, veterinary x-ray systems are specifically designed to cater to the needs of different animal species, considering their varying anatomy and size, while also ensuring minimal exposure to ionizing radiation.
The Importance of X-Rays in Veterinary Medicine
X-rays play a pivotal role in veterinary medicine by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and facilitating timely interventions. They are indispensable in diagnosing commonplace conditions such as arthritis, dental disease, and trauma in pets. Moreover, by providing clear images of soft tissue and bony structures, x-rays help veterinarians formulate effective treatment plans. The ability to detect issues that cannot be evaluated through physical examinations alone significantly improves the quality of care for animals. The use of advanced veterinary x-ray systems has further augmented this capability, allowing for better quality images and faster results, which are crucial for emergency cases.
Types of Veterinary X-Ray Systems
Veterinary x-ray systems come in various forms, each designed to meet specific needs within a veterinary practice. The main types include:
- Analog X-Ray Systems: Older technology that utilizes traditional film and requires chemical processing to develop images.
- Digital X-Ray Systems: More modern and efficient, digital x-ray systems utilize digital sensors to produce images instantaneously, reducing waiting times and allowing immediate diagnosis.
- Portable X-Ray Systems: Compact and lightweight, these systems offer mobility, making them suitable for fieldwork and emergency situations, particularly in farm veterinary settings.
- Stand-Alone X-Ray Units: These systems are designated for specific practices, allowing for focused use and tailored features, such as enhanced imaging for dental or orthopedic applications.
Benefits of Advanced Veterinary X-Ray Systems
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
Advanced veterinary x-ray systems significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy. Digital x-ray technology boasts improved image resolution and clarity, enabling veterinarians to detect subtle abnormalities that might be missed with traditional analog systems. This enhanced precision is crucial for early detection of conditions like tumors or fractures, leading to better treatment outcomes. Moreover, many systems come equipped with software tools for image enhancement, allowing for a thorough evaluation of complex cases.
Faster Imaging Techniques
Time is often of the essence in veterinary care, particularly in emergencies. Modern digital x-ray systems provide rapid imaging capabilities, allowing veterinarians to obtain and analyze images in real time. This speed not only streamlines workflow within veterinary practices but also enhances the overall experience for pet owners, providing them with immediate insights into their pet’s condition. The integration of automations, such as pre-set protocols for various animal types, further speeds up the imaging process.
Client Education and Communication
Effective communication with pet owners is vital for fostering trust and enhancing the overall client experience. Advanced veterinary x-ray systems facilitate this by allowing veterinarians to show images and explain findings directly to clients. Access to visual documentation of health issues helps clients understand the diagnosis better and makes them more likely to commit to treatment. Furthermore, many systems support the storage and sharing of images, which can be useful for referrals to specialists.
Choosing the Right Veterinary X-Ray System for Your Practice
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right veterinary x-ray system is critical for ensuring optimal diagnostic capabilities. Some key factors to consider include:
- Animal Size and Types: Ensure the system caters to the range of animals you typically handle, from small pets to larger livestock.
- Space and Mobility: Consider your practice’s physical layout. A portable x-ray unit might be beneficial for limited space, while a fixed system may be better suited for larger clinics.
- User-Friendliness: Select a system that is intuitive and easy to operate, minimizing the learning curve for your veterinary staff.
Budget Considerations
Budget is a critical element when selecting a veterinary x-ray system. While advanced systems often come with higher initial costs, it’s essential to evaluate their return on investment. Consider factors like operation costs, maintenance, and longevity of the system. Digital systems, for example, may have a higher upfront cost but can save money in the long run through reduced film and processing expenses.
Vendor Comparisons
When evaluating potential x-ray system vendors, it’s crucial to compare warranties, customer service reputations, and the availability of technical support and training. Reading reviews from other veterinary practices can aid in making a more informed decision. Additionally, trial periods are beneficial for assessing functionality before making a long-term commitment.
Best Practices for Operating Veterinary X-Ray Systems
Training Staff for Efficient Use
Comprehensive training for staff operating the veterinary x-ray system is paramount. This not only includes understanding how to use the system but also involves learning about radiation safety and patient positioning. Continuous education ensures that all team members are up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices in imaging technology.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is essential for maintaining the integrity of the x-ray images produced. Regular maintenance checks should be performed on the equipment to ensure it functions optimally. Implementing protocols for image evaluation can help identify any inconsistencies early on, and adopting a routine calibration schedule is vital to preserving image quality.
Safety Protocols for Animals and Staff
Safety should always be a primary concern when operating veterinary x-ray systems. Staff must adhere to radiation safety protocols, including the use of lead aprons, shielding techniques, and monitoring exposure levels. Additionally, creating a calm environment for animals during imaging procedures helps mitigate stress, ensuring better cooperation and more accurate positioning.
Future Trends in Veterinary X-Ray Technology
Emerging Technologies in Imaging
The field of veterinary x-ray technology is rapidly evolving. Emerging technologies include portable ultrasound and advanced imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which may integrate with standard x-ray systems for comprehensive evaluations. Innovations like artificial intelligence (AI) are becoming prevalent, aiding in image analysis and early condition detection.
Integration with Telemedicine
As telemedicine continues to gain traction, the integration of x-ray systems with telehealth platforms is on the rise. This allows veterinarians to share imaging results with specialists or remote clients instantaneously, facilitating second opinions without requiring physical visits. This trend not only enhances diagnostics but contributes significantly to improved patient care and convenience for pet owners.
Enhancements in Image Processing Software
Advancements in image processing software are revolutionizing how veterinary x-rays are interpreted and archived. Modern software solutions offer powerful tools for manipulating images, enabling veterinarians to enhance contrast, zoom in on specific areas, and view three-dimensional models of anatomical structures. These capabilities support detailed assessment and improve diagnostic precision.