Understanding Precision Die Cutting
Precision die cutting is a sophisticated manufacturing process that converts materials into custom shapes with unparalleled accuracy. It’s extensively used across various industries for producing components that require precision and consistency. This method ensures that products not only meet stringent quality standards but also reduces the overall production time. By understanding the nuances of precision die cutting, manufacturers can tailor their processes to achieve optimal results for their products.
What is Precision Die Cutting?
Precision die cutting involves the use of specialized blades or dies to cut materials into specific shapes. This process can utilize a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, rubber, textiles, and metals. Unlike traditional cutting methods, precision die cutting focuses on the accuracy of the shape and size, ensuring minimal tolerance levels. The ability to produce complex shapes efficiently makes it a preferred method in industries like automotive, electronics, and packaging.
Key Components of Die Cutting Machines
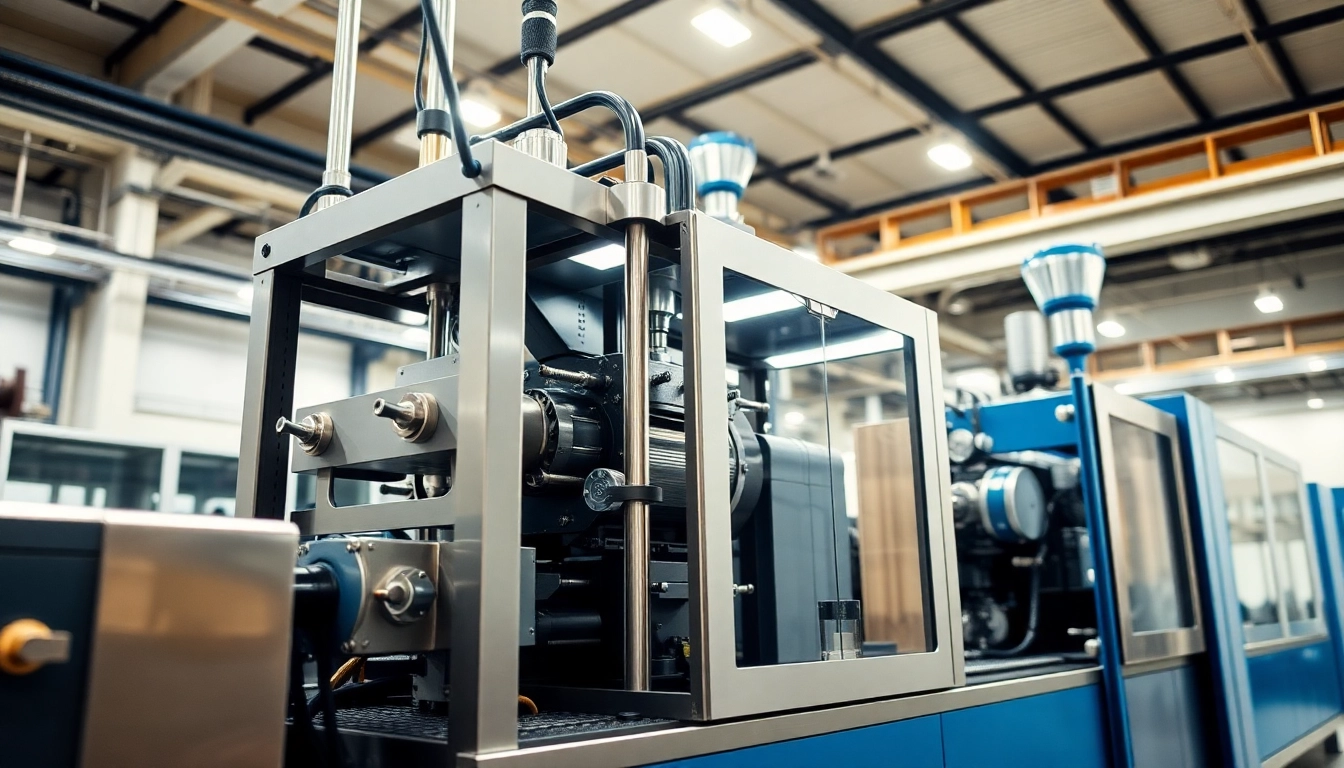
Understanding the components of a die cutting machine is essential to mastering precision die cutting. Here are the main parts:
- Die: The mold that shapes the material during cutting. Dies can be flat, rotary, or laser-cut.
- Press: The machine that applies pressure to the die, performing the cutting action.
- Material Feed System: This mechanism feeds the material into the machine, ensuring a consistent supply during the cutting process.
- Control Systems: Modern die cutting machines often feature computerized controls that enable precise adjustments and automation.
- Collection System: After cutting, this system collects and organizes the finished products, enhancing work efficiency.
Applications Across Industries
Precision die cutting is not limited to one sector; its versatility is evident across multiple industries:
- Automotive: Used to produce gaskets, seals, and insulators, ensuring efficiency and safety in vehicles.
- Electronics: Creates intricate parts like connectors and insulators that require high precision.
- Medical: Essential for manufacturing sterile packaging and components for medical devices, adhering to strict quality standards.
- Packaging: Helps in creating custom packaging solutions that meet specific design and functionality requirements.
- Textiles: Employed in fashion and upholstery to cut complex designs efficiently.
Types of Precision Die Cutting Techniques
Flatbed Die Cutting: Advantages and Limitations
Flatbed die cutting involves a flat bed press that applies force to cut materials with flat dies. This method is ideal for thicker materials and offers several advantages:
- Versatility: Can accommodate a wide range of materials, including thick substrates.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Suitable for both short and long production runs.
- Simplicity: Easier setup and maintenance compared to other die-cutting methods.
However, it has limitations, including slower production speeds compared to rotary die cutting and less precision for intricate designs.
Rotary Die Cutting: The Efficient Choice
Rotary die cutting uses a cylindrical die mounted on a rotating drum, making it an efficient choice for high-speed production. Its advantages include:
- Speed: Ideal for large volume runs, significantly reducing production time.
- Precision: Provides consistent cuts with lower tolerances, suited for intricate designs.
- Reduced Waste: More efficient material usage, minimizing production waste.
Despite its advantages, rotary die cutting may have a higher initial setup cost and is best suited for larger production runs.
Comparing Laser and Conventional Methods
Laser die cutting has gained popularity due to its precision and flexibility. Traditional methods, such as flatbed and rotary die cutting, hold their own benefits. Here’s a comparison:
| Features | Laser Die Cutting | Conventional Die Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High | Moderate to High |
| Setup Cost | Higher | Varies, generally lower for flatbed |
| Production Speed | Moderate | High (especially rotary) |
| Material Versatility | High | Moderate (depends on machine) |
Laser cutting provides the advantage of cutting complex shapes without the need for physical dies, which can be ideal for prototyping and small runs. However, it might not always match the speed of rotary or flatbed machines for large volume tasks.
Benefits of Precision Die Cutting
High Tolerance and Accuracy Standards
One of the standout benefits of precision die cutting is its ability to achieve tight tolerances. Many industries require components that can perform under intense conditions, and the precision achieved in die cutting allows for improved product performance and reliability.
Cost Efficiency in Production
By optimizing material usage and minimizing waste, precision die cutting reduces costs significantly. Additionally, the quick turnaround times allow manufacturers to fulfill orders rapidly, generating faster revenue and improving cash flow.
Customization Options for Various Materials
Precision die cutting can accommodate a diverse range of materials, allowing companies to customize their products according to specific requirements. This flexibility is essential in catering to niche markets, providing tailored solutions that meet unique client needs.
Challenges in the Precision Die Cutting Process
Managing Material Waste and Costs
Despite its advantages, precision die cutting can pose challenges related to material waste. Manufacturers need to utilize advanced software and efficient designs to optimize material usage and reduce excess waste. Regular training on best practices can also mitigate this issue.
Ensuring Consistent Quality Control
Maintaining high quality across runs is crucial, particularly in industries like automotive and medical. Implementing stringent quality control measures, including inspections at various stages, can ensure consistency and reliability. Automated quality control systems can significantly enhance precision in manufacturing.
Overcoming Setup Time for Different Designs
Setting up for different designs can be time-consuming, especially when switching between die types. Adopting advanced die cutting systems that feature quick-change die capabilities can streamline this process, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Future Trends in Precision Die Cutting
Integration of Automation and AI
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in precision die cutting will transform the industry. AI can optimize cutting paths, predict maintenance needs, and enhance precision, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Automated systems can facilitate faster changeovers and minimize manual labor.
Sustainability in Die Cutting Practices
As environmental consciousness grows, manufacturers are focusing on sustainable practices. Utilizing eco-friendly materials, optimizing waste reduction, and recycling scrap can enhance sustainability in precision die cutting operations. Adopting energy-efficient machines also contributes to greener practices.
Evolving Customer Demands and Custom Solutions
As industries evolve, so do customer demands for tailored solutions. Precision die cutting will need to adapt to these changes, offering customizable options for various applications. Continuous engagement with clients to understand their evolving needs can steer manufacturers in the right direction, ensuring their offerings remain relevant and competitive.